A) homologous chromosomes
B) nonhomologous chromosomes
C) sister chromatids
D) complementary strands of DNA
E) maternal and paternal copies of the same chromosome
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During meiosis I:
A) bivalents are formed during prophase I and are taken apart during anaphase I.
B) chromosomes undergo reductional division.
C) sister chromatids are not separated.
D) non-sister chromatids exchange maternal and paternal DNA.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first oncogene to be discovered:
A) is a gene that contributes to uncontrolled cell division or cancer.
B) was discovered in a Rous sarcoma virus that causes cancer.
C) is a protein kinase that acts to promote cell division.
D) has a less-active normal counterpart called a proto-oncogene.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During what step in meiosis do the daughter cells become haploid?
A) metaphase II
B) anaphase I
C) anaphase II
D) prophase II
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paramecium is a single-cell eukaryotic organism that can reproduce by mitotic cell division. Prior to the M phase of the cell cycle, which of the following must occur?
A) The cell must replicate its chromosomes.
B) The cell must first be fertilized.
C) The nucleus must divide.
D) Sister chromatids must be separated.
E) The nuclear envelope must disintegrate.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscle cells in the mammalian heart are multinucleate, meaning that multiple nuclei are present in the cytoplasm of a large cell. Predict what is different about the cell cycle in a muscle cell.
A) The G1 and G2 phases are extended.
B) Cytokinesis does not occur.
C) S phase happens twice.
D) M phase is inhibited.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In fungi and plants, mitotic cell division of haploid cells follows meiosis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is circled in this electron micrograph? 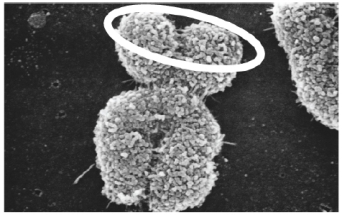 Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
Photo credit: Biophoto Associates/Science Source
A) one double-stranded DNA molecule
B) one single strand of a DNA molecule
C) two double-stranded DNA molecules
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if a defect in S phase occurred during cell division?
A) There could be too few chromosomes.
B) There could be too many chromosomes.
C) There could be a lack of cytoplasm.
D) All organelles may not be duplicated.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do CDKs promote cell division?
A) They regulate the activity of cyclin.
B) They cause cyclin levels to increase and decrease.
C) They bind to DNA.
D) They phosphorylate other proteins.
E) They change the ability of microtubules to polymerize.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
p53 is an example of a(n) :
A) oncogene.
B) proto-oncogene.
C) tumor suppressor.
D) cyclin-dependent kinase.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true about gametes?
A) They are formed by meiotic cell division.
B) They have half as many chromosomes as a somatic cell of the same individual.
C) They are called eggs and sperm in animals.
D) They fuse to form a new organism during fertilization.
E) They are genetically identical to other gametes formed during meiosis.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell in prophase I of meiosis has _____ as many chromosomes as each of the daughter cells following cytokinesis of meiosis II.
A) twice
B) half
C) one quarter
D) four times
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell that is not actively dividing is in what phase of the cell cycle?
A) G1
B) G0
C) G1'
D) G2
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the start of mitosis, how many sister chromatids are present in a human cell?
A) 23
B) 92
C) 46
D) 12
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given that the correct number of chromosomes is vital to the proper functioning of a cell, which of the statements below is CORRECT if a cell passes from G1 to S phase in the cell cycle?
A) The cell copies its chromosomes and enters G2 or it returns to G1.
B) The cell completes the process of cell division or it dies.
C) The cell divides or it returns to G1 and enters G0.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What cellular process(es) is/are responsible for the increase in protein content associated with the gap phases of the cell cycle?
A) gene expression
B) glycolysis
C) protein synthesis
D) both gene expression and protein synthesis
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope reform?
A) prophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) telophase
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a step in the process of binary fission?
A) replication of DNA
B) formation of a new cell wall
C) rearrangement of the microtubule cytoskeleton
D) elongation of the cell
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The division of genetic material in a eukaryotic cell is called:
A) genetic fission.
B) mitosis.
C) cytokinesis.
D) replication.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 169
Related Exams