A) 3.162
B) 1.645
C) 1.860
D) 2.132
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The difference between two sample proportions p1 − p2 may be assumed normally distributed if each sample has at least 10 "successes" and 10 "failures."
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the sample proportions were p1 = 12/50 and p2 = 18/50,what is the approximate 95 percent confidence interval for the difference of the population proportions?
A) [−.144,+.244]
B) [−.120,+.120]
C) [−.298,+.058]
D) [−.011,.214]
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coach of an adult Master's Swim class selected eight swimmers within each of the two age groups shown below.A 50-yard freestyle time is recorded for each swimmer.The resulting times (seconds) are shown below.Which statistical test would you choose to compare the two groups? 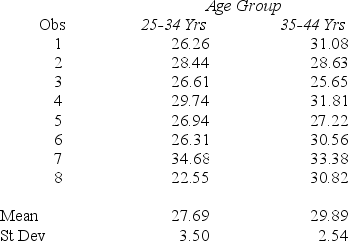
A) t-test for independent samples with known variances
B) t-test for independent samples with unknown variances
C) t-test for paired samples
D) z-test for two independent proportions
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A certain psychological theory predicts that men want bigger families than women.Kate asked each student in her psychology class how many children he or she considered ideal for a married couple and obtained the Excel results shown below at α = .05. 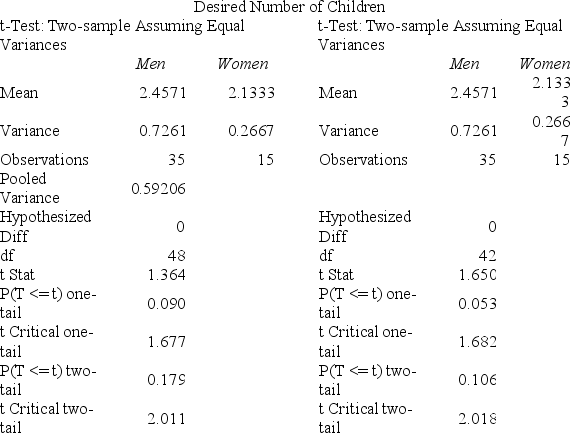 What conclusion can you draw in a two-tailed test at α = .05?
What conclusion can you draw in a two-tailed test at α = .05?
A) Men want larger families on average than women.
B) Women want larger families on average than men.
C) We cannot reject the hypothesis of equal population means.
D) The decision depends on whether or not the variances are equal.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a test of a new surgical procedure,the five most respected surgeons in FlatBroke Township were invited to Carver Hospital.Each surgeon was assigned two patients of the same age,gender,and overall health.One patient was operated upon in the old way,and the other in the new way.Both procedures are considered equally safe.The surgery times are shown below: Which test should we use to test for zero difference in mean times? 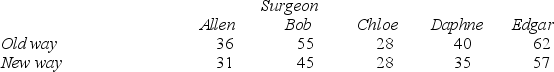 Which test should we use to test for zero difference in mean times?
Which test should we use to test for zero difference in mean times?
A) Use the paired t-test.
B) Use the independent samples t-test.
C) Use the independent samples z test.
D) Cannot be sure which test to use without knowing α.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the sample proportions are p1 = 6/90 and p2 =4/100,normality may be assumed in a test comparing the two population proportions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A psychology researcher has a theory that predicts women will tend to carry more cash than men.A random sample of Ersatz University students revealed that 16 females had a mean of $22.30 in their wallets with a standard deviation of $3.20,while 16 males had a mean of $17.30 with a standard deviation of $9.60.The test statistic for the researcher's hypothesis is
A) impossible to determine without knowing α.
B) 1.250
C) 1.504
D) 1.976
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of 200 youthful gamers (under 18) who tried the new Z-Box-Plus game,160 rated it "excellent," compared with only 144 of 200 adult gamers (18 or over) .The pooled proportion for a test to compare the two proportions would be
A) .76
B) .72
C) .77
D) Must know α to answer.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A medical researcher compared the variances in birth weights for five randomly chosen babies of each gender,with the MegaStat results shown below. 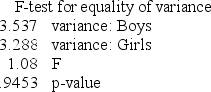 The population variances
The population variances
A) may be assumed equal at any customary a.
B) should be assumed unequal at any customary a.
C) are not relevant to this paired t-test.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the mean number of daily errors by air traffic controller trainees during the first two weeks on the job.We want to perform a paired t-test at α = .05 to see if the mean daily errors decreased significantly.  What would be the degrees of freedom for the appropriate test?
What would be the degrees of freedom for the appropriate test?
A) 14
B) 12
C) 7
D) 6
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At Huge University,a sample of 200 business school seniors showed that 26 planned to pursue an MBA degree,compared with 120 of 800 arts and sciences seniors.We want to know if the proportion is higher in the arts and sciences group.What is the z test statistic?
A) −1.322
B) −1.122
C) −0.716
D) We must first know α.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the population variances are exactly equal,the sample F test statistic will be zero.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a random sample of patient records in Cutter Memorial Hospital,six-month postoperative exams were given in 90 out of 200 prostatectomy patients,while in Paymor Hospital such exams were given in 110 out of 200 cases.In comparing these two proportions,normality of the difference may be assumed because
A) the populations are large enough to be assumed normal.
B) the probability of success can reasonably be assumed constant.
C) the samples are random,so the proportions are unbiased estimates.
D) nπ ≥ 10 and n(1 − π) ≥ 10 for each sample taken separately.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows two samples taken to compare the mean age of individuals who purchased the iPhone 3G at two AT&T store locations. 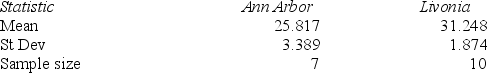 What are the critical values for a two-tailed test for equal variances at α = .05?
What are the critical values for a two-tailed test for equal variances at α = .05?
A) 0.275,3.14
B) 0.244,3.37
C) 0.210,3.95
D) 0.181,4.32
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nacirema Airlines is buying a fleet of new fuel-efficient planes.The HogJet and the LitheJet both meet their price and performance needs,and both planes meet EPA noise guidelines.However,the quieter plane is preferred.Each plane is flown through a typical takeoff and landing sequence 10 times,while remote sensors at ground level record the noise levels (in decibels) .The table below summarizes the sound level tests using Excel's default level of significance (α = .05) .  After inspecting this table,we would most likely
After inspecting this table,we would most likely
A) use the test assuming unequal variances.
B) use the test for equal variances.
C) perform another test to determine if the variances are equal before proceeding.
D) realize that the decision is not affected by our assumptions concerning the variance.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which Excel function would give the critical value for a left-tailed F test to compare two sample variances?
A) =F.INV(α,df1,df2)
B) =F.DIST(s12/s22,df1,df2)
C) =F.INV(α/2,df1,df2)
D) =1−F.DIST(s12/s22,df1,df2)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
John wants to compare two means.His sample statistics were ![John wants to compare two means.His sample statistics were 1 = 22.7,s12 = 5.4,n1 = 9 and 2 = 20.5,s22 = 3.6,n2 = 9.Assuming equal variances,which is the approximate 95 percent confidence interval for the difference of the population means? A) [2.44,6.19] B) [1.17,5.08] C) [0.08,4.32] D) [−0.09,3.19]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6743/11eaab07_12f2_47ae_acdb_fd73a8797215_TB6743_11.jpg) 1 = 22.7,s12 = 5.4,n1 = 9 and
1 = 22.7,s12 = 5.4,n1 = 9 and ![John wants to compare two means.His sample statistics were 1 = 22.7,s12 = 5.4,n1 = 9 and 2 = 20.5,s22 = 3.6,n2 = 9.Assuming equal variances,which is the approximate 95 percent confidence interval for the difference of the population means? A) [2.44,6.19] B) [1.17,5.08] C) [0.08,4.32] D) [−0.09,3.19]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6743/11eaab07_12f2_6ebf_acdb_493a14c1d3f4_TB6743_11.jpg) 2 = 20.5,s22 = 3.6,n2 = 9.Assuming equal variances,which is the approximate 95 percent confidence interval for the difference of the population means?
2 = 20.5,s22 = 3.6,n2 = 9.Assuming equal variances,which is the approximate 95 percent confidence interval for the difference of the population means?
A) [2.44,6.19]
B) [1.17,5.08]
C) [0.08,4.32]
D) [−0.09,3.19]
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not true of the two-tailed F-test for equality of variances?
A) It requires reversing the numerator and denominator d.f.to obtain the left-tail critical value.
B) It can be avoided by "folding" the larger variance into the numerator and adjusting α.
C) It is fairly robust to the presence of nonnormality in the populations being sampled.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The F test is used to test for the equality of two population variances.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 116
Related Exams