A) mtDNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) tRNA
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT synthesized from a DNA template?
A) messenger RNA
B) amino acids
C) transfer RNA
D) ribosomal RNA
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product?
A) a deletion of a codon
B) a deletion of two nucleotides
C) a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
D) a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
E) an insertion of a codon
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mutation resulting in sickle cell disease changes one base pair of DNA so that a codon now codes for a different amino acid, making it an example of a ________.
A) nonsense mutation
B) frameshift mutation
C) silent mutation
D) missense mutation
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
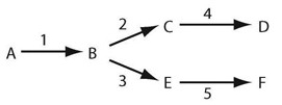 Refer to the associated figure. A branched metabolic pathway synthesizes two related amino acids (D and F) If there is a genetic defect, resulting in a nonfunctional enzyme (3) , how could you ensure that adequate amounts of the amino acid F are synthesized?
Refer to the associated figure. A branched metabolic pathway synthesizes two related amino acids (D and F) If there is a genetic defect, resulting in a nonfunctional enzyme (3) , how could you ensure that adequate amounts of the amino acid F are synthesized?
A) supplement intermediate B
B) supplement intermediate C
C) add enzyme 2 to the medium
D) supplement with intermediate E
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) refer to this table of codons. 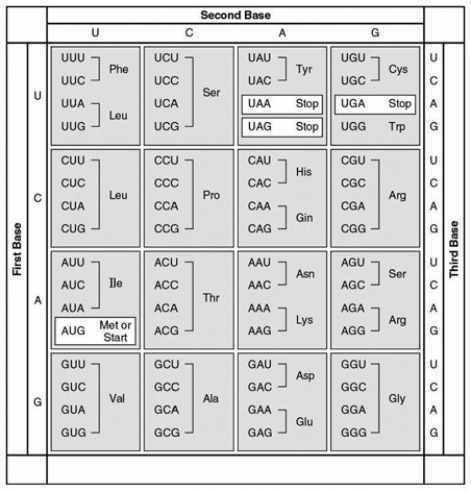 -A peptide has the sequence NH2-phe-pro-lys-gly-phe-pro-COOH. Which of the following sequences in the coding strand of the DNA could code for this peptide?
-A peptide has the sequence NH2-phe-pro-lys-gly-phe-pro-COOH. Which of the following sequences in the coding strand of the DNA could code for this peptide?
A) 3' UUU-CCC-AAA-GGG-UUU-CCC
B) 3' AUG-AAA-GGG-TTT-CCC-AAA-GGG
C) 5' TTT-CCC-AAA-GGG-TTT-CCC
D) 5' GGG-AAA-TTT-AAA-CCC-ACT-GGG
E) 5' ACT-TAC-CAT-AAA-CAT-TAC-UGA
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5' AGT 3'. The corresponding codon for the mRNA transcribed is ________.
A) 3' UCA 5'
B) 3' UGS 5'
C) 5' TCA 3'
D) 3' ACU 5'
E) either UCA or TCA, depending on wobble in the first base
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why might a point mutation in DNA make a difference in the level of a protein's activity?
A) It might result in a chromosomal translocation.
B) It might exchange one stop codon for another stop codon.
C) It might delay the rate of DNA replication.
D) It might substitute a different amino acid in the active site.
E) It might substitute the N-terminus of the polypeptide for the C-terminus.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
HIV, the causative agent of AIDS, is a retrovirus. A retrovirus ________.
A) uses DNA as a template in the process of translation
B) makes proteins directly from RNA
C) uses reverse transcriptase to make DNA from RNA
D) is a cellular virus that uses ribosomes to reproduce inside a living cell
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Knockout mice have been genetically altered to knock out specific genes. How are these mice most often used in research?
A) to study DNA replication in the defective genes (those that have been altered)
B) to determine the role of proteins coded for by those genes that are knocked out
C) to examine defects in DNA structure in those regions that have been altered
D) to study the effect of radiation on DNA
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the process of transcription, ________.
A) DNA is replicated
B) RNA is synthesized
C) proteins are synthesized
D) mRNA attaches to ribosomes
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation that results in premature termination of translation ________.
A) is a silent mutation
B) is a nonsense mutation
C) usually has no effect on the function of the protein
D) is a missense mutation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
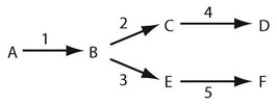 Refer to the associated figure. In the branched metabolic pathway indicated in the figure, if enzyme 3 is defective and the amount of each enzyme is constant, you might expect to see an increase in the amount of which intermediate or product?
Refer to the associated figure. In the branched metabolic pathway indicated in the figure, if enzyme 3 is defective and the amount of each enzyme is constant, you might expect to see an increase in the amount of which intermediate or product?
A) E
B) B
C) F
D) D
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Morse code, a series of dots and dashes code for letters of the alphabet. How is this analogous to the genetic code?
A) There is complementarity in the genetic code (A is complementary to T, and C is complementary to G) .
B) The bases that make up DNA are coded by the sugar-phosphate backbone.
C) The machinery involved in DNA synthesis is analogous to the telegraph equipment used in sending Morse code.
D) The bases of DNA code for the more complex amino acid sequence of the proteins in cells.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Point mutations are referred to as missense, silent, frameshift, or nonsense when they change the protein-coding potential of a gene. What is another group of mutations that may have important consequences for gene expression?
A) mutations that exist outside coding sequences
B) combinations of missense and silent mutations
C) combinations of nonsense and silent mutations
D) mutations that alter the amino acid sequence of a gene
E) mutations that shift the reading frame of a gene
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genotype is to ________ as phenotype is to ________.
A) DNA base sequence; physical traits that are products of the proteins produced
B) heredity; DNA base sequence
C) gene regulation; translation
D) transcription; amino acid sequence
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have a harmful effect on an organism?
A) a nucleotide-pair substitution
B) a deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene
C) a single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron
D) a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
E) a single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the simple primary and secondary structure of DNA hold the information needed to code for the many features of multicellular organisms?
A) The hydrogen bonding among backbone constituents carries coded information.
B) The base sequence of DNA carries the information needed to code for proteins.
C) The width of the double helix changes at each gene due to differences in hydrogen bonds.
D) The amino acids that make up the DNA molecule contain the information needed to make cellular proteins.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the first step of their experiments, Jacob and Monod treated E. coli cells with ultraviolet light or X-rays to ________.
A) decrease the rate of gene expression
B) induce DNA repair enzymes
C) increase the frequency of mutations in all genes
D) selectively mutate specific genes, leaving all other genes unmutated
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
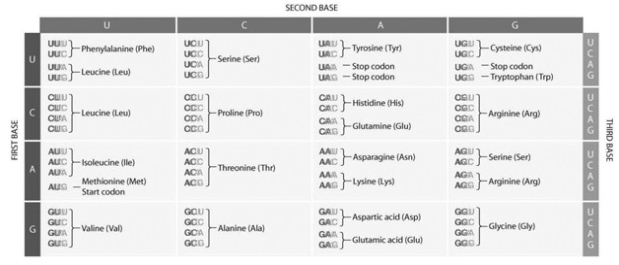 Consider the following section of mRNA:
UCUGAUGGGCUUU…
Beginning with the start codon, which amino acids, in order, are coded for by this section of mRNA? Consult the codon table provided if necessary.
Consider the following section of mRNA:
UCUGAUGGGCUUU…
Beginning with the start codon, which amino acids, in order, are coded for by this section of mRNA? Consult the codon table provided if necessary.
A) serine, aspartic acid, glycine, leucine
B) methionine, glycine, phenylalanine
C) methionine, valine, glycine, phenylalanine
D) threonine, methionine, glycine
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 48
Related Exams