A) −2.2 μC
B) +6.7 μC
C) −2.7 μC
D) +8.0 μC
E) −1.1 μC
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform linear density 3.0 nC/m is distributed along the x axis from x = 0 to x = 3 m.Which of the following integrals is correct for the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the point x = +4 m on the x axis?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A charge of 18 nC is uniformly distributed along the y axis from y = 3 m to y = 5 m.Which of the following integrals is correct for the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the point x = +2 m on the x axis?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A charge is placed on a spherical conductor of radius r1.This sphere is then connected to a distant sphere of radius r2 (not equal to r1) by a conducting wire.After the charges on the spheres are in equilibrium,
A) the electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres are equal.
B) the amount of charge on each sphere is q/2.
C) both spheres are at the same potential.
D) the potentials are in the ratio ![]() .
.
E) the potentials are in the ratio ![]() .
.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Point charges of equal magnitudes (25 nC) and opposite signs are placed on (diagonally) opposite corners of a 60-cm × 80-cm rectangle.If point A is the corner of this rectangle nearest the positive charge and point B is located at the intersection of the diagonals of the rectangle,determine the potential difference,VB − VA.
A) −47 V
B) +94 V
C) zero
D) −94 V
E) +47 V
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several charges in the neighborhood of point P produce an electric potential of 6.0 kV (relative to zero at infinity) and an electric field of 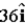 N/C at point P.Determine the work required of an external agent to move a 3.0-μC charge along the x axis from infinity to point P without any net change in the kinetic energy of the particle.
N/C at point P.Determine the work required of an external agent to move a 3.0-μC charge along the x axis from infinity to point P without any net change in the kinetic energy of the particle.
A) 21 mJ
B) 18 mJ
C) 24 mJ
D) 27 mJ
E) 12 mJ
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two identical particles,each with a mass of 2.0 μg and a charge of 25 nC,are released simultaneously from rest when the two are 4.0 cm apart.What is the speed of either particle at the instant when the two are separated by 10 cm?
A) 7.3 m/s
B) 9.8 m/s
C) 9.2 m/s
D) 6.5 m/s
E) 4.6 m/s
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A system consisting of a negatively-charged particle and an electric field
A) gains potential difference and kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
B) loses electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
C) gains kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
D) gains electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
E) gains potential difference and electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electric field in the region defined by the y-z plane and the negative x axis is given by E = −ax,where a is a constant.(There is no field for positive values of x. ) As −x increases in magnitude,relative to V = 0 at the origin,the electric potential in the region defined above is
A) a decreasing function proportional to −|x2|.
B) a decreasing function proportional to −|x|.
C) constant.
D) an increasing function proportional to +|x|.
E) an increasing function proportional to +|x2|.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identical 4.0-μC charges are placed on the y axis at y = ±4.0 m.Point A is on the x axis at x = +3.0 m.Determine the electric potential of point A (relative to zero at the origin) .
A) −4.5 kV
B) −2.7 kV
C) −1.8 kV
D) −3.6 kV
E) −14 kV
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle (charge = +2.0 mC) moving in a region where only electric forces act on it has a kinetic energy of 5.0 J at point A.The particle subsequently passes through point B which has an electric potential of +1.5 kV relative to point A.Determine the kinetic energy of the particle as it moves through point B.
A) 3.0 J
B) 2.0 J
C) 5.0 J
D) 8.0 J
E) 10.0 J
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a = 30 cm,b = 20 cm,q = +2.0 nC,and Q = −3.0 nC in the figure,what is the potential difference VA − VB? 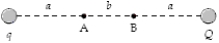
A) +60 V
B) +72 V
C) +84 V
D) +96 V
E) +48 V
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron (m = 9.1 × 10−31 kg,q = −1.6 × 10−19 C) starts from rest at point A and has a speed of 5.0 × 106 m/s at point B.Only electric forces act on it during this motion.Determine the electric potential difference VA − VB.
A) −71 V
B) +71 V
C) −26 V
D) +26 V
E) −140 V
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform linear density 6.0 nC/m is distributed along the x axis from x = 0 to x = +3 m.Which of the following integrals is correct for the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at the point y = +4 m on the y axis?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electric potential inside a charged solid spherical conductor in equilibrium
A) is always zero.
B) is constant and equal to its value at the surface.
C) decreases from its value at the surface to a value of zero at the center.
D) increases from its value at the surface to a value at the center that is a multiple of the potential at the surface.
E) is equal to the charge passing through the surface per unit time divided by the resistance.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When introduced into a region where an electric field is present,an electron with initial velocity 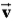 Will eventually move
Will eventually move
A) along an electric field line,in the positive direction of the line.
B) along an electric field line,in the negative direction of the line.
C) to a point of decreased potential.
D) to a point of increased potential.
E) as described in both (b) and (d) .
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two particles,each having a mass of 3.0 μg and having equal but opposite charges of magnitude 5.0 nC,are released simultaneously from rest when the two are 5.0 cm apart.What is the speed of either particle at the instant when the two are separated by 2.0 cm?
A) 2.1 m/s
B) 1.5 m/s
C) 1.8 m/s
D) 2.4 m/s
E) 3.2 m/s
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle (charge = 50 μC) moves in a region where the only force on it is an electric force.As the particle moves 25 cm from point A to point B,its kinetic energy increases by 1.5 mJ.Determine the electric potential difference,VB − VA.
A) −50 V
B) −40 V
C) −30 V
D) −60 V
E) +15 V
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is always correct when applied to a charge distribution located in a finite region of space?
A) Electric potential is always zero at infinity.
B) Electric potential is always zero at the origin.
C) Electric potential is always zero at a boundary surface to a charge distribution.
D) Electric potential is always infinite at a boundary surface to a charge distribution.
E) The location where electric potential is zero may be chosen arbitrarily.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rod (length = 2.0 m) is uniformly charged and has a total charge of 5.0 nC.What is the electric potential (relative to zero at infinity) at a point which lies along the axis of the rod and is 3.0 m from the center of the rod?
A) 22 V
B) 19 V
C) 16 V
D) 25 V
E) 12 V
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 97
Related Exams