A) Modified Cleaves method
B) Clements-Nakayama
C) Danelius-Miller
D) Judet method
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the correct gender to correspond with the following pelvic characteristics.Round and large pelvic inlet:
A) Male
B) Female
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radiograph of an AP axial (Taylor) "outlet" projection reveals that the obturator foramina are not symmetric.What type of positioning error is present on this radiograph?
A) Tilt of the pelvis
B) Off-center CR
C) Rotation of the pelvis
D) Probable fracture of the pubis or ischium
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radiograph of an axiolateral (inferosuperior) projection reveals that there is an excessive amount of grid lines present.A 6:1 linear grid was used.Which of the following points will correct this problem on the repeat exposure?
A) Use a screen rather than a grid.
B) Decrease the SID.
C) Keep the image receptor and grid parallel to the femoral neck and perpendicular to the CR.
D) Keep the image receptor and grid perpendicular to the femoral neck.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient enters the ER with a possible pelvic ring fracture due to an MVA.The initial pelvis projections do not reveal any fracture or dislocation, but the ER physician is concerned about a possible right acetabular fracture.Which of the following projections will best demonstrate the right acetabulum?
A) AP axial inlet projection
B) Axiolateral inferosuperior projection (Danelius-Miller method)
C) Modified axiolateral projection (Clements-Nakayama method)
D) Posterior oblique pelvis projection (Judet method)
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The posterior oblique (Judet method) for the acetabulum requires a 10° to 15° rotation of the body.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the labeled structures is the obturator foramen? 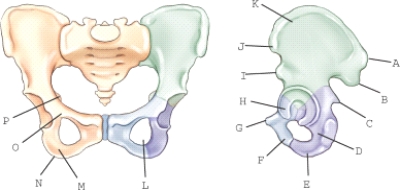
A) H
B) L
C) E
D) O
E) P
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures is considered to be most inferior or distal?
A) Fovea capitis
B) Lesser trochanter
C) Neck
D) Greater trochanter
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following projections will best demonstrate a lateral oblique view of the femoral head and neck for the patient with limited movement in both lower limbs?
A) Teufel
B) Axiolateral (inferosuperior) projection
C) AP axial (Taylor)
D) Modified axiolateral (Clements-Nakayama)
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A study of a prosthetic hip demonstrates that the end of the prosthesis is cut off on the AP projection, but the entire device is demonstrated on the lateral projection.What should the technologist do next?
A) Repeat both the AP and lateral projections.
B) Repeat the AP projection only.
C) Ask another technologist for his or her opinion.
D) Ask the radiologist if he or she wants the AP projection repeated.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which bone of the pelvis forms the anterior inferior aspect?
A) Ilium
B) Ischium
C) Pubis
D) Sacrum
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following imaging modalities will best detect early signs of bone infection of the pelvis?
A) Radiography
B) CT
C) Nuclear medicine
D) MRI
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a repeat study of the AP axial (Taylor) outlet projection, both obturator foramina are symmetric but foreshortened.Which of the following positioning modifications must be performed to correct this error?
A) Increase the cephalic CR angulation.
B) Increase the caudad CR angulation.
C) Correct for rotation.
D) Use a perpendicular CR.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a patient has excessive external rotation of one foot, a fractured hip may be indicated.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use of the 80 to 90 kV (analog) technique (as opposed to 70 kV) with a corresponding mAs change for an AP pelvis projection will result in:
A) increased radiographic contrast.
B) improved spatial resolution.
C) reduction in gonadal dose.
D) none of the above; the difference is not measurable.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radiograph of an axiolateral (inferosuperior) projection of the hip reveals a soft tissue artifact seen across the affected hip.This artifact prevents a clear view of the femoral head and neck.What must the technologist do to eliminate this artifact or its effect during the repeat exposure?
A) Increase the kV.
B) Ensure that the CR is centered to the grid to prevent grid cutoff.
C) Increase the elevation and flexion of the patient's unaffected leg.
D) Slightly rotate the patient toward the affected side and angle 5° caudad.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the correct gender to correspond with the following pelvic characteristics.An 80° to 85° angle of pubic arch:
A) Male
B) Female
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two bony landmarks that are palpated using the hip localization method are the:
A) ischial spine and the symphysis pubis.
B) symphysis pubis and the greater trochanter.
C) ASIS and the crest of ilium.
D) ASIS and the symphysis pubis.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the correct disease or condition with the corresponding pathologic description. (Use each choice only once.) -A degenerative joint disease
A) Metastatic carcinoma
B) Ankylosing spondylitis
C) Congenital dislocation of hip
D) Chondrosarcoma
E) Pelvic ring fracture
F) Osteoarthritis
G) Avulsion fracture
I) C) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proper name of the method used for the unilateral frog-leg projection is the _____ method.
A) Danelius-Miller
B) modified Cleaves
C) Teufel
D) Taylor
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 80
Related Exams