A) respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) maintain cell pressure
D) contain DNA
E) synthesize lipids
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein secretion from prokaryotic cells?
A) Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to secrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system.
B) The mechanism of protein secretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in eukaryotes.
C) Proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane.
D) In prokaryotes, the ribosomes that are used for the synthesis of secreted proteins are located outside of the cell.
E) Prokaryotes contain large pores in their plasma membrane that permit the movement of proteins out of the cell.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Signals between the ECM and the cytoskeleton may be transmitted by
A) fibronectin.
B) proteoglycans.
C) integrins.
D) collagen.
E) middle lamella.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. What are the domains?
A) Bacteria and Eukarya
B) Bacteria and Archaea
C) Archaea and Protista
D) Bacteria and Protista
E) Bacteria and Fungi
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following makes it necessary for animal cells, although they have no cell walls, to have intercellular junctions?
A) Cell membranes do not distinguish the types of ions and molecules passing through them.
B) Large molecules, such as proteins and RNA molecules, do not readily get through one, much less two, adjacent cell membranes.
C) Cell-to-cell communication requires physical attachment of one cell to another.
D) Maintenance of tissue integrity and barriers to fluid leakage requires cells to adhere tightly to one another.
E) The relative shapelessness of animal cells requires a mechanism for keeping the cells aligned.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytochalasin D is a drug that prevents actin polymerization. A cell treated with cytochalasin D will still be able to
A) perform amoeboid movement.
B) form cleavage furrows.
C) contract muscle fibres.
D) extend pseudopodia.
E) move vesicles around the cell.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If radioactive deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) is added to a culture of rapidly growing bacterial cells, where in the cell would you expect to find the greatest concentration of radioactivity?
A) nucleus
B) cytoplasm
C) endoplasmic reticulum
D) nucleoid
E) ribosomes
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
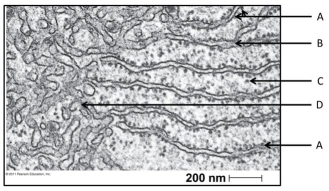 -In the figure above, identify the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
-In the figure above, identify the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) The RER is not visible on this image.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which organelle often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell?
A) lysosome
B) vacuole
C) mitochondrion
D) Golgi apparatus
E) peroxisome
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which plant cell organelle contains its own DNA and ribosomes?
A) glyoxysome
B) vacuole
C) mitochondrion
D) Golgi apparatus
E) peroxisome
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -The image above is a ________ image.
-The image above is a ________ image.
A) light microscope
B) phase contrast
C) scanning electron micrograph
D) transmission electron micrograph
E) confocal
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vinblastine, a drug that inhibits microtubule polymerization, is used to treat some forms of cancer. Cancer cells given vinblastine would be unable to
A) form cleavage furrows during cell division.
B) migrate by amoeboid movement.
C) separate chromosomes during cell division.
D) extend pseudopods.
E) maintain the shape of the nucleus.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The smallest unit of matter that can be considered alive is the/a
A) nucleic acid.
B) mitochondria.
C) virus.
D) cell.
E) organism.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The extracellular matrix is thought to participate in the regulation of animal cell behaviour by communicating information from the outside to the inside of the cell via which of the following?
A) gap junctions
B) the nucleus
C) DNA and RNA
D) integrins
E) plasmodesmata
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell except
A) DNA.
B) a cell wall.
C) a plasma membrane.
D) ribosomes.
E) an endoplasmic reticulum.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
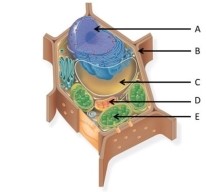 -What type of cell is pictured above?
-What type of cell is pictured above?
A) Archaea
B) Bacteria
C) protist
D) plant
E) animal
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a potassium ion (K⁺) moves from the soil into the vacuole of a cell on the surface of a root, it must pass through several cellular structures. Which of the following correctly describes the order in which these structures will be encountered by the ion?
A) plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
B) secondary cell wall → plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
C) primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → vacuole
D) primary cell wall → plasma membrane → lysosome → cytoplasm → vacuole
E) primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → secondary cell wall → vacuole
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A biologist wants specifically to examine the surfaces of different types of cells in kidney tubules of small mammals. The cells in question can be distinguished by external shape, size, and 3-D characteristics. Which of the following would be the optimum method for her study?
A) transmission electron microscopy
B) cell fractionation
C) light microscopy using stains specific to kidney function
D) light microscopy of living unstained material
E) scanning electron microscopy
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules, consisting of nine doublets of microtubules surrounding a pair of single microtubules?
A) both motile cilia and primary (nonmotile) cilia
B) centrioles only
C) both flagella and motile cilia
D) both basal bodies and primary (nonmotile) cilia
E) both centrioles and basal bodies
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of organelle or structure is primarily involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids?
A) ribosome
B) lysosome
C) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D) mitochondrion
E) contractile vacuole
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 96
Related Exams