A) mRNA
B) tRNA
C) rRNA
D) pre-mRNA
E) hnRNA
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transcription unit that is 8,000 nucleotides long may use 1,200 nucleotides to make a protein consisting of approximately 400 amino acids. This is best explained by the fact that
A) many noncoding stretches of nucleotides are present in mRNA.
B) there is redundancy and ambiguity in the genetic code.
C) many nucleotides are needed to code for each amino acid.
D) nucleotides break off and are lost during the transcription process.
E) there are termination exons near the beginning of mRNA.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule?
A) covalent bonding between sulfur atoms
B) ionic bonding between phosphates
C) hydrogen bonding between base pairs
D) van der Waals interactions between hydrogen atoms
E) peptide bonding between amino acids
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene?
A) It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
B) It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
C) It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
D) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA.
E) It prevents introns from being excised.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to Figure 17.2, a table of codons.
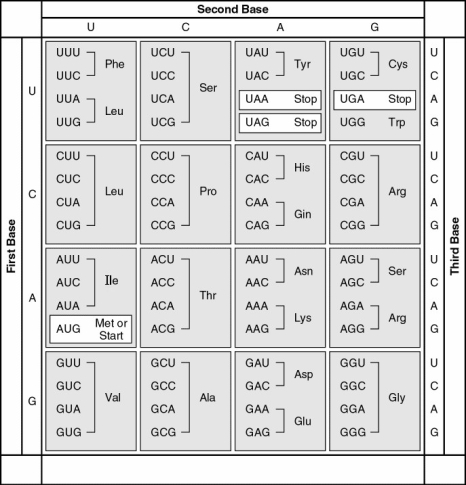 -What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
-What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
A) met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
B) met-glu-arg-arg-gln-leu
C) met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
D) met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
E) met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria occur because
A) genes dictate the production of specific enzymes, and affected individuals have genetic defects that cause them to lack certain enzymes.
B) enzymes are made of DNA, and affected individuals lack DNA polymerase.
C) many metabolic enzymes use DNA as a cofactor, and affected individuals have mutations that prevent their enzymes from interacting efficiently with DNA.
D) certain metabolic reactions are carried out by ribozymes, and affected individuals lack key splicing factors.
E) metabolic enzymes require vitamin cofactors, and affected individuals have significant nutritional deficiencies.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When translating secretory or membrane proteins, ribosomes are directed to the ER membrane by
A) a specific characteristic of the ribosome itself, which distinguishes free ribosomes from bound ribosomes.
B) a signal-recognition particle that brings ribosomes to a receptor protein in the ER membrane.
C) moving through a specialized channel of the nucleus.
D) a chemical signal given off by the ER.
E) a signal sequence of RNA that precedes the start codon of the message.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following actions does RNA polymerase differ from DNA polymerase?
A) RNA polymerase uses RNA as a template, and DNA polymerase uses a DNA template.
B) RNA polymerase binds to single-stranded DNA, and DNA polymerase binds to double-stranded DNA.
C) RNA polymerase is much more accurate than DNA polymerase.
D) RNA polymerase can initiate RNA synthesis, but DNA polymerase requires a primer to initiate DNA synthesis.
E) RNA polymerase does not need to separate the two strands of DNA in order to synthesize an RNA copy, whereas DNA polymerase must unwind the double helix before it can replicate the DNA.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume all of the following except
A) a gene from an organism could theoretically be expressed by any other organism.
B) all organisms have a common ancestor.
C) DNA was the first genetic material.
D) the same codons in different organisms usually translate into the same amino acids.
E) different organisms have the same number of different types of amino acids.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the answer that has these events of protein synthesis in the proper sequence. 1. An aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A site. 2) A peptide bond forms between the new amino acid and a polypeptide chain. 3) tRNA leaves the P site, and the P site remains vacant. 4) A small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA. 5) tRNA translocates to the P site.
A) 1, 3, 2, 4, 5
B) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3
C) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
D) 4, 1, 3, 2, 5
E) 2, 4, 5, 1, 3
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are 61 mRNA codons that specify an amino acid, but only 45 tRNAs. This is best explained by the fact that
A) some tRNAs have anticodons that recognize four or more different codons.
B) the rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA are flexible.
C) many codons are never used, so the tRNAs that recognize them are dispensable.
D) the DNA codes for all 61 tRNAs but some are then destroyed.
E) competitive exclusion forces some tRNAs to be destroyed by nucleases.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions. A transfer RNA (#1) attached to the amino acid lysine enters the ribosome. The lysine binds to the growing polypeptide on the other tRNA (#2) in the ribosome already. -When the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA, no corresponding tRNA enters the A site. If the translation reaction were to be experimentally stopped at this point, which of the following would you be able to isolate?
A) an assembled ribosome with a polypeptide attached to the tRNA in the P site
B) separated ribosomal subunits, a polypeptide, and free tRNA
C) an assembled ribosome with a separated polypeptide
D) separated ribosomal subunits with a polypeptide attached to the tRNA
E) a cell with fewer ribosomes
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to Figure 17.5, a table of codons.
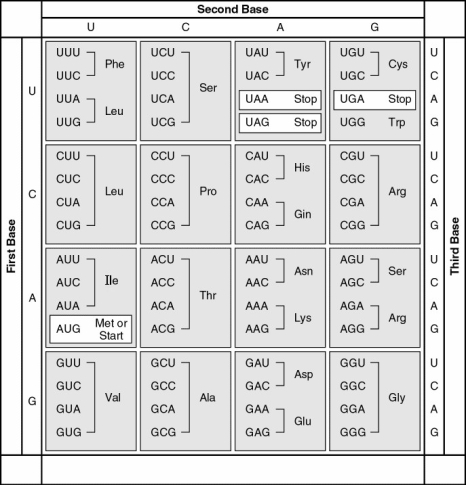 Figure 17.5
-Using Figure 17.5, identify a 5' → 3' sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
Figure 17.5
-Using Figure 17.5, identify a 5' → 3' sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
A) 5'-UUUGGGAAA-3'
B) 5'-GAACCCCTT-3'
C) 5'-AAAACCTTT-3'
D) 5'-CTTCGGGAA-3'
E) 5'-AAACCCUUU-3'
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on specificity in the
A) binding of ribosomes to mRNA.
B) shape of the A and P sites of ribosomes.
C) bonding of the anticodon to the codon.
D) attachment of amino acids to tRNAs.
E) both C and D
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome catalyzes the excision reaction?
A) protein
B) DNA
C) RNA
D) lipid
E) sugar
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following DNA mutations is the most likely to be damaging to the protein it specifies?
A) a base-pair deletion
B) a codon substitution
C) a substitution in the last base of a codon
D) a codon deletion
E) a point mutation
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a function of a signal peptide?
A) to direct an mRNA molecule into the cisternal space of the ER
B) to bind RNA polymerase to DNA and initiate transcription
C) to terminate translation of the messenger RNA
D) to translocate polypeptides across the ER membrane
E) to signal the initiation of transcription
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is True for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression?
A) After transcription, a 3' poly-A tail and a 5' cap are added to mRNA.
B) Translation of mRNA can begin before transcription is complete.
C) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region to begin transcription.
D) mRNA is synthesized in the 3' → 5' direction.
E) The mRNA transcript is the exact complement of the gene from which it was copied.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions. A transfer RNA (#1) attached to the amino acid lysine enters the ribosome. The lysine binds to the growing polypeptide on the other tRNA (#2) in the ribosome already. -Where does tRNA #2 move to after this bonding of lysine to the polypeptide?
A) A site
B) P site
C) E site
D) Exit tunnel
E) Directly to the cytosol
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the following questions. A transfer RNA (#1) attached to the amino acid lysine enters the ribosome. The lysine binds to the growing polypeptide on the other tRNA (#2) in the ribosome already. -Why might a point mutation in DNA make a difference in the level of protein's activity?
A) It might result in a chromosomal translocation.
B) It might exchange one stop codon for another stop codon.
C) It might exchange one serine codon for a different serine codon.
D) It might substitute an amino acid in the active site.
E) It might substitute the N terminus of the polypeptide for the C terminus.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 84
Related Exams