A) detachment
B) normal
C) reverse
D) thrust
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An episode of mountain building is termed a(n) ________.
A) orogeny
B) phylogeny
C) aureole
D) slickenside
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a geologic map,if the contacts between sedimentary rock units form a bull's-eye pattern of concentric circles,with the oldest unit in the center,the underlying structure is a(n) ________. 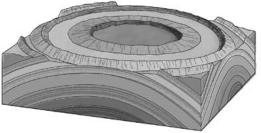
A) anticline
B) basin
C) dome
D) syncline
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A polished surface produced by scraping of rock along a fault is termed a(n) ________.
A) orogeny
B) phylogeny
C) aureole
D) slickenside
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Regularly spaced joints in an outcrop may indicate that an area ________.
A) is under intense shear stress
B) has experienced compressional stress
C) is underlain by a thrust fault
D) is formed from rocks that were once at great depth
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normal,reverse,and thrust are all examples of ________ faults.
A) strike-slip
B) dip-slip
C) oblique-slip
D) lateral
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a fault plane is less than 35° from horizontal and the hanging-wall block moves upward relative to the footwall block,the fault is a ________ fault.
A) detachment
B) normal
C) reverse
D) thrust
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A body of rock affected by tensile stress will likely undergo ________.
A) shortening
B) stretching
C) shear strain
D) rotation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is stress different from strain?
A) Strain is a measure of the total displacement on a fault.
B) Stress is the change in shape of a rock due to applied strain.
C) Strain is the change in shape of a rock due to applied stress.
D) They are not different: stress and strain are synonymous.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fold shaped like an elongate arch is a(n) ________. 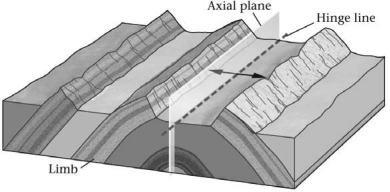
A) anticline
B) basin
C) dome
D) syncline
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these features would NOT help a geologist recognize a fault?
A) different rock units juxtaposed against each other
B) a small step on the landscape
C) a shattered rock consisting of visible angular fragments
D) regularly spaced quartz veins
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the map below,the vertical,north-south trending fault is a ________ fault. 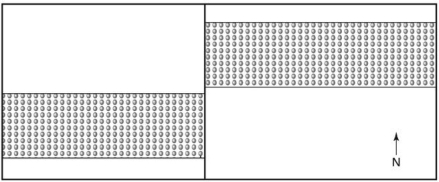
A) normal dip-slip
B) reverse dip-slip
C) right-lateral strike-slip
D) left-lateral strike-slip
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How were nearly all of the present mountain ranges formed?
A) tilting of rift blocks into half grabens
B) compression of areas along transform plate boundaries
C) addition of accreted terranes to the continents
D) repeated cycles of collision and rifting
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are many ways in which uplift can occur,but all of them reflect ________.
A) compressional forces
B) the effects of weathering and erosion
C) subduction zone processes
D) the lithosphere's tendency to achieve isostasy
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is tectonic foliation,such as elongation of quartz grains,oriented relative to the original bedding plane of a body of rock?
A) Foliation is parallel to original bedding.
B) Foliation is at about 45° to original bedding.
C) Foliation is perpendicular to original bedding.
D) Foliation can be at a variety of angles to original bedding.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is stress different from force?
A) Force is the stress applied per unit area.
B) Stress is the force applied per unit area.
C) Force comes from one direction,while stress comes from all directions.
D) They are not different: stress and force are synonymous.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Shear stress at sufficient depth within a fault plane can induce plastic shear,forming a fine-grained metamorphic rock named ________.
A) ignimbrite
B) gneiss
C) mylonite
D) migmatite
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Force per unit area is termed ________.
A) stress
B) strain
C) power
D) work
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Orogenesis (mountain building) leads to the production of ________.
A) metamorphic rocks
B) igneous and sedimentary rocks
C) metamorphic and igneous rocks
D) igneous,metamorphic,and sedimentary rocks
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a geologic map,if the contacts between sedimentary rock units form a bull's-eye pattern of concentric circles,with the youngest unit in the center,the underlying structure is a(n) ________. 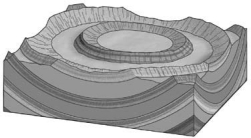
A) anticline
B) basin
C) dome
D) syncline
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 50
Related Exams