A) external rotation.
B) internal rotation.
C) abduction.
D) adduction.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For delineation of the body of the scapula for the lateral projection, how is the arm positioned?
A) Flex the elbow and place the hand on the anterior abdomen.
B) Flex the elbow and place the hand on the posterior thorax.
C) Extend the arm straight down at the side.
D) Extend the arm upward and rest the forearm on the head.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To obtain a more uniform image density, the respiration phase for the AP projection of the clavicle should be:
A) inspiration.
B) expiration.
C) shallow breathing.
D) suspended respiration.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use of compensating filters is particularly useful when using:
A) small focal spot.
B) digital radiography systems.
C) detail film/screen IR.
D) less collimation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Hill-Sachs defect is a:
A) fracture due to posterior dislocation of the humeral head.
B) wedge-shaped compression fracture of the articular surface of the humeral head.
C) congenital deformity of the humeral head.
D) congenital deformity of the glenoid cavity.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For an AP projection of the scapula, the IR size and its position should be:
A) 8 * 10 inches (18 * 24 cm) lengthwise.
B) 10 * 12 inches (24 * 30 cm) lengthwise.
C) 8 * 10 inches (18 * 24 cm) crosswise.
D) 10 * 12 inches (24 * 30 cm) crosswise.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The glenoid of the scapula in the image below is labeled as letter:
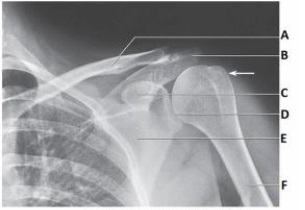
A) B.
B) C.
C) D.
D) E.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the central-ray angulation for the AP oblique projection (Grashey method) of the shoulder joint?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees
C) 0 to 5 degrees
D) 5 to 10 degrees
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For delineation of the acromion and coracoid processes of the scapula in the lateral projection, how is the arm positioned?
A) Flex the elbow and place the hand on the anterior abdomen.
B) Flex the elbow and place the hand on the posterior thorax.
C) Extend the arm upward and rest the forearm on the head.
D) Extend the arm straight down at the side in the anatomic position.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will be directly superimposed over the junction of the Y on the PA oblique (scapular Y) projection?
A) Humerus
B) Humeral head
C) Coracoid process
D) Acromion process
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following methods best demonstrates the supraspinatus outlet (coracoacromial arch) ?
A) Neer
B) Alexander
C) West Point
D) Stryker notch
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following projections clearly demonstrates the glenoid cavity?
A) AP
B) PA oblique (scapular Y)
C) AP oblique (Grashey)
D) Transthoracic lateral (Lawrence)
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the patient cannot elevate the unaffected shoulder for a transthoracic lateral projection of the shoulder, the central ray should be angled _____ degrees.
A) 0 to 5
B) 5 to 10
C) 10 to 15
D) 15 to 25
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How should the central ray be angled for the AP projection (Pearson method) of the AC joints?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees cephalad
C) 7 degrees cephalad
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Letter B in the image below labels the:
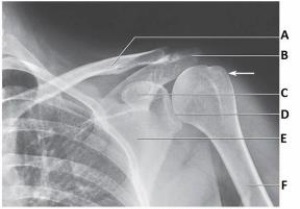
A) acromion.
B) coracoid process.
C) clavicle.
D) glenoid.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The scapulohumeral articulation is classified as a _____ joint, _____ type.
A) cartilaginous; gliding
B) fibrous; gliding
C) synovial; ball and socket
D) synovial; condyloid
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is the central ray directed for an inferosuperior axial projection of the shoulder joint?
A) 5 degrees horizontally
B) 15 to 30 degrees horizontally
C) 5 degrees cephalad
D) 15 to 30 degrees cephalad
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greater tubercle will be partially superimposed over the humeral head on which of the following projections and positions?
A) AP, external rotation
B) AP, neutral rotation
C) AP, internal rotation
D) PA oblique, scapular Y
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following projections are improved significantly with the use of a compensating filter? 1) AP shoulder 2) Lateral scapula 3) PA oblique (scapular Y)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lateral projection of the shoulder and proximal humerus can be obtained with which of the following?
A) PA oblique (scapular Y)
B) Inferosuperior axial (Lawrence)
C) Inferosuperior axial (West Point)
D) Transthoracic lateral (Lawrence)
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 92
Related Exams