A) to direct an mRNA molecule into the cisternal space of the ER
B) to bind RNA polymerase to DNA and initiate transcription
C) to terminate translation of the messenger RNA
D) to translocate polypeptides across the ER membrane
E) to signal the initiation of transcription
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What molecular structure are codons part of?
A) a protein
B) mRNA
C) tRNA
D) rRNA
E) DNA
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "universal" genetic code is now known to have exceptions.Evidence for this can be found if which of the following is true?
A) If UGA, usually a stop codon, is found to code for an amino acid such as tryptophan (usually coded for by UGG only) .
B) If one stop codon, such as UGA, is found to have a different effect on translation than another stop codon, such as UAA.
C) If prokaryotic organisms are able to translate a eukaryotic mRNA and produce the same polypeptide.
D) If several codons are found to translate to the same amino acid, such as serine.
E) If a single mRNA molecule is found to translate to more than one polypeptide when there are two or more AUG sites.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information should be used for the next few questions.
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5' CCG-ACG 3' (mRNA) .The following charged transfer RNA molecules (with their anticodons shown in the 3' to 5' direction) are available.Two of them can correctly match the mRNA so that a dipeptide can form.
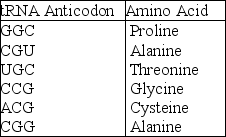 -The anticodon loop of the first tRNA that will complement this mRNA is
-The anticodon loop of the first tRNA that will complement this mRNA is
A) 3' GGC 5'
B) 5' GGC 3'
C) 5' ACG 3'
D) 5' UGC 3'
E) 3' UGC 5'
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations is most likely to cause a phenotypic change?
A) a duplication of all or most introns
B) a large inversion whose ends are each in intergenic regions
C) a nucleotide substitution in an exon coding for a transmembrane domain
D) a single nucleotide deletion in an exon coding for an active site
E) a frameshift mutation one codon away from the 3' end of the nontemplate strand
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contradicts the one-gene,one-enzyme hypothesis?
A) A mutation in a single gene can result in a defective protein.
B) Alkaptonuria results when individuals lack a single enzyme involved in the catalysis of homogentisic acid.
C) Sickle-cell anemia results in defective hemoglobin.
D) A single antibody gene can code for different related proteins, depending on the splicing that takes place post-transcriptionally.
E) Two enzymes are able to metabolize the same reaction.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During elongation,which site in the ribosome represents the location where a codon is being read?
A) E site
B) P site
C) A site
D) the small ribosomal subunit
E) exit site
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following provides some evidence that RNA probably evolved before DNA?
A) RNA polymerase uses DNA as a template.
B) RNA polymerase makes a single-stranded molecule.
C) RNA polymerase does not require localized unwinding of the DNA.
D) DNA polymerase uses primer, usually made of RNA.
E) DNA polymerase has proofreading function.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Yeast is capable of synthesizing the amino acids necessary for survival and can grow on minimal media or enriched media easily.In both conditions,the colonies have a cream colour.The production of adenine is regulated by two genes,ADE1 and ADE2.If either of these genes is defective,adenine cannot be synthesized and the colony will look red (as a result of accumulation of precursors) .A common undergraduate lab study is to irradiate yeast cells with ultra violet light from 2-5 sec up to 1-5 minutes,and see what will happen. -What is the role of UV light in this circumstance?
A) It is a promoter.
B) It functions in RNA splicing.
C) It initiates RNA interference.
D) It is a mutagen.
E) It blocks tumour suppression.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why might a point mutation in DNA make a difference in the level of protein's activity?
A) It might result in a chromosomal translocation.
B) It might exchange one stop codon for another stop codon.
C) It might exchange one serine codon for a different serine codon.
D) It might substitute an amino acid in the active site.
E) It might substitute the N-terminus of the polypeptide for the C-terminus.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. The enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase randomly assembles nucleotides into a polynucleotide polymer. -You add polynucleotide phosphorylase to a solution of ATP,GTP,and UTP.How many artificial mRNA 3 nucleotide codons would be possible?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 27
E) 81
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transcription in eukaryotes requires which of the following in addition to RNA polymerase?
A) the protein product of the promoter
B) start and stop codons
C) ribosomes and tRNA
D) several transcription factors (TFs)
E) aminoacyl synthetase
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The TATA sequence is found approximately 25 nucleotides upstream from the start site of transcription.This most probably relates to which of the following?
A) its involvement with binding the transcription factor that helps place polymerase II in the correct location
B) its direct binding of polymerase II
C) the ability of this sequence to bind to the start site
D) the supercoiling of the DNA near the start site
E) the 3-D shape of a DNA molecule
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The white fur colouration of the "spirit bear" of British Columbia,is a result of
A) a point mutation, leading to a missense protein.
B) a point mutation leading to a nonsense protein.
C) albinism.
D) a deletion in the MC1 chromosome.
E) hybridization with polar bears.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the function of the newly made polypeptide is to be secreted from the cell where it has been made,what must occur?
A) It must be translated by a ribosome that remains free of attachment to the ER.
B) Its signal sequence must target it to the ER, from which it goes to the Golgi.
C) It has a signal sequence that must be cleaved off before it can enter the ER.
D) It has a signal sequence that targets it to the cell's plasma membrane where it causes exocytosis.
E) Its signal sequence causes it to be encased in a vesicle as soon as it is translated.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following,if missing,would usually prevent translation from starting?
A) exon
B) 5' cap
C) AUG codon
D) poly-A tail
E) ATP
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
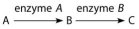 -If A,B,and C are all required for growth,a strain mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme B would be capable of growing on which of the following media?
-If A,B,and C are all required for growth,a strain mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme B would be capable of growing on which of the following media?
A) minimal medium
B) minimal medium supplemented with A only
C) minimal medium supplemented with B only
D) minimal medium supplemented with C only
E) minimal medium supplemented with nutrients A and B
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to this figure of a simple metabolic pathway:
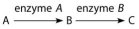 -If A,B,and C are all required for growth,a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
-If A,B,and C are all required for growth,a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
A) minimal medium
B) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient A only
C) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient B only
D) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient C only
E) minimal medium supplemented with nutrients A and C
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do eukaryotic codons and prokaryotic codons compare?
A) Prokaryotic codons usually contain different bases than those of eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotic codons usually specify different amino acids than those of eukaryotes.
C) The translation of codons is mediated by tRNAs in eukaryotes, but translation requires no intermediate molecules such as tRNAs in prokaryotes.
D) Codons are a nearly universal language among all organisms.
E) Eukaryotic codons require ribosomes for translation while prokaryotic codons do not.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene?
A) It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
B) It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
C) It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
D) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA.
E) It prevents introns from being excised.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 106
Related Exams