A) autotrophs released O₂ from the splitting of CO₂ to make sugars.
B) autotrophs didn't use CO₂.
C) CO₂ was released and oxygen used up during photosynthesis.
D) only heterotrophs released O₂ while fixing carbon.
E) the process of photosynthesis was unknown at this time.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If plant gene alterations cause the plants to be deficient in photorespiration,what would most probably occur?
A) Photosynthetic efficiency would be reduced at low light intensities.
B) Cells would carry on the Calvin cycle at a much slower rate.
C) Less ATP would be generated.
D) There would be more light-induced damage to the cells.
E) Less oxygen would be produced.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis,it is a direct by-product of
A) reducing NADP⁺.
B) splitting water molecules.
C) chemiosmosis.
D) the electron transfer system of photosystem I.
E) the electron transfer system of photosystem II.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur during the Calvin cycle?
A) carbon fixation
B) oxidation of NADPH
C) release of oxygen
D) regeneration of the CO₂ acceptor
E) consumption of ATP
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Theodor W.Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism,thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light.He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated.He noted that the largest groups were found in the areas illuminated by the red and blue light. -An outcome of this experiment was to help determine
A) the relationship between heterotrophic and autotrophic organisms.
B) the relationship between wavelengths of light and the rate of aerobic respiration.
C) the relationship between wavelengths of light and the amount of heat released.
D) the relationship between wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis.
E) the relationship between the concentration of carbon dioxide and the rate of photosynthesis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CO₂ + H₂O → [CH₂O] + O₂ represents the simplified equation for
A) chemiosmosis.
B) chemisynthesis.
C) photosynthesis.
D) photophosphorylation.
E) respiration.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
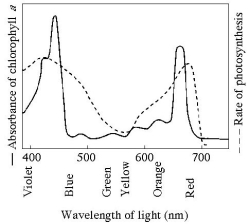 -The figure above shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis.Why are they different?
-The figure above shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis.Why are they different?
A) Green and yellow wavelengths inhibit the absorption of red and blue wavelengths.
B) Bright sunlight destroys photosynthetic pigments.
C) Oxygen given off during photosynthesis interferes with the absorption of light.
D) Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
E) Aerobic bacteria take up oxygen, which changes the measurement of the rate of photosynthesis.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure and the compounds labelled A,B,C,D,and E to answer the following questions.
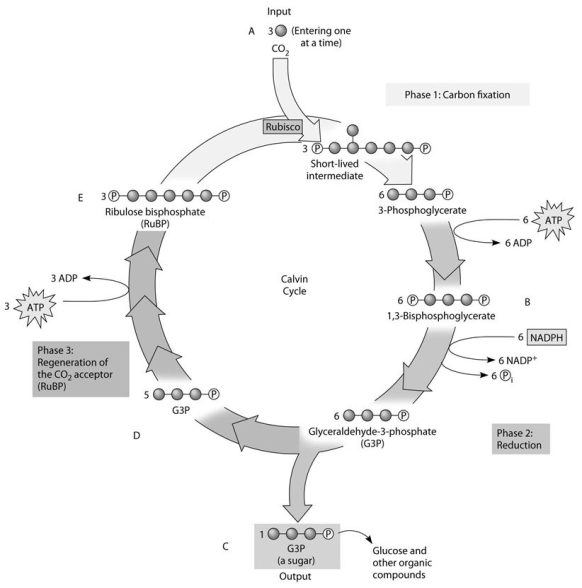 -To identify the molecule that accepts CO₂,Calvin and Benson manipulated the carbon-fixation cycle by either cutting off CO₂ or cutting off light from cultures of photosynthetic algae.They then measured the concentrations of various metabolites immediately following the manipulation.How would these experiments help identify the CO₂ acceptor? Study the figure above to help you in determining the correct answer.
-To identify the molecule that accepts CO₂,Calvin and Benson manipulated the carbon-fixation cycle by either cutting off CO₂ or cutting off light from cultures of photosynthetic algae.They then measured the concentrations of various metabolites immediately following the manipulation.How would these experiments help identify the CO₂ acceptor? Study the figure above to help you in determining the correct answer.
A) The CO₂ acceptor concentration would decrease when either the CO₂ or light are cut off.
B) The CO₂ acceptor concentration would increase when either the CO₂ or light are cut off.
C) The CO₂ acceptor concentration would increase when the CO₂ is cut off, but decrease when the light is cut off.
D) The CO₂ acceptor concentration would decrease when the CO₂ is cut off, but increase when the light is cut off.
E) The CO₂ acceptor concentration would stay the same regardless of the CO₂ or light.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reduction of oxygen to form water occurs during
A) photosynthesis only.
B) respiration only.
C) both photosynthesis and respiration.
D) neither photosynthesis nor respiration.
E) photorespiration only.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma.This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?
A) the splitting of water
B) the absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
C) the flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I
D) the synthesis of ATP
E) the reduction of NADP⁺
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In autotrophic bacteria,where is chlorophyll located?
A) in chloroplast membranes
B) in the ribosomes
C) in the nucleoid
D) in the plasma membrane
E) in the chloroplast thylakoids
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When do plants split water providing a source of electrons and protons?
A) only in the light
B) only in the dark
C) in both the light and dark
D) only if oxygen is present
E) in both the light and dark, but only if oxygen is present
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the events listed below occurs in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
A) NADP is produced.
B) NADPH is reduced to NADP⁺.
C) Carbon dioxide is incorporated into 3-phosphoglycerate.
D) ATP is phosphorylated to yield ADP.
E) Light is absorbed and funnelled to reaction-centre chlorophyll a.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In any ecosystem,terrestrial or aquatic,what group(s) is (are) always necessary?
A) autotrophs and heterotrophs
B) producers and primary consumers
C) photosynthesizers
D) autotrophs
E) green plants
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure and the compounds labelled A,B,C,D,and E to answer the following questions.
 -Which molecule(s) of the Calvin cycle is (are) also found in glycolysis?
-Which molecule(s) of the Calvin cycle is (are) also found in glycolysis?
A) B, C, E, and 3-phosphoglycerate
B) B, C, and E only
C) 3-phosphoglycerate only
D) B, C, D, and 3-phosphoglycerate only
E) E only
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phylogenetic distribution of the enzyme Rubisco is limited to
A) C₃ plants only.
B) C₃ and C₄ plants.
C) all photosynthetic eukaryotes.
D) all known photoautotrophs, both bacterial and eukaryotic.
E) all living cells.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are directly associated with photosystem I?
A) harvesting of light energy by ATP
B) receiving electrons from the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
C) generation of molecular oxygen
D) extraction of hydrogen electrons from the splitting of water
E) passing electrons to the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system.Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide. -If the power fails and the lights go dark,what will happen to CO₂ levels?
A) CO₂ will rise as a result of both animal and plant respiration.
B) CO₂ will rise as a result of animal respiration only.
C) CO₂ will remain balanced because plants will continue to fix CO₂ in the dark.
D) CO₂ will fall because plants will increase CO₂ fixation.
E) CO₂ will fall because plants will cease to respire in the dark.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What did the accumulation of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere began with?
A) the origin of life and respiratory metabolism
B) cyanobacteria using photosystem II
C) chloroplasts in photosynthetic eukaryotic algae
D) land plants
E) the breakdown of CO₂
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
A) Respiration runs the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis in reverse.
B) Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, whereas respiration releases it.
C) Photosynthesis occurs only in plants and respiration occurs only in animals.
D) ATP molecules are produced in photosynthesis and used up in respiration.
E) Respiration is anabolic and photosynthesis is catabolic.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 103
Related Exams