A) 0, 0.
B) ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
C) ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
D) given in any answer above.
E) given only in answer (a) or (b) above.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform surface density (0.20 nC/m2) is distributed over the entire xy plane. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at any point having z = 2.0 m.
A) 17 N/C
B) 11 N/C
C) 23 N/C
D) 28 N/C
E) 40 N/C
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform linear density (4.0 nC/m) is distributed along the entire x axis. Determine the magnitude of the electric field on the y axis at y = 2.5 m.
A) 36 N/C
B) 29 N/C
C) 43 N/C
D) 50 N/C
E) 58 N/C
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniformly charged rod (length = 2.0 m, charge per unit length = 5.0 nC/m) is bent to form one quadrant of a circle. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the center of the circle?
A) 62 N/C
B) 56 N/C
C) 50 N/C
D) 44 N/C
E) 25 N/C
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform surface density (4.0 nC/m2) is distributed on a spherical surface (radius = 2.0 cm) . What is the total electric flux through a concentric spherical surface with a radius of 4.0 cm?
A) 2.8 N ⋅ m2/C
B) 1.7 N ⋅ m2/C
C) 2.3 N ⋅ m2/C
D) 4.0 N ⋅ m2/C
E) 9.1 N ⋅ m2/C
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform density (40 pC/m2) is distributed on a spherical surface (radius = 1.0 cm) , and a second concentric spherical surface (radius = 3.0 cm) carries a uniform charge density of 60 pC/m2. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 2.0 cm from the center of the two surfaces?
A) 1.1 N/C
B) 4.5 N/C
C) 1.4 N/C
D) 5.6 N/C
E) 0.50 N/C
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of a uniform density (8.0 nC/m2) is distributed over the entire xy plane. A charge of uniform density (3.0 nC/m2) is distributed over the parallel plane defined by z = 2.0 m. Determine the magnitude of the electric field for any point with z = 3.0 m.
A) 0.79 kN/C
B) 0.17 kN/C
C) 0.62 kN/C
D) 0.34 kN/C
E) 0.28 kN/C
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student has made the statement that the electric flux through one half of a Gaussian surface is always equal to the flux through the other half of the Gaussian surface. This is
A) never true.
B) never false.
C) true whenever enclosed charge is symmetrically located at a center point, on a center line, or on a centrally placed plane.
D) true whenever no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
E) true only when no charge is enclosed within the Gaussian surface.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The nucleus of lead-208,  , has 82 protons within a sphere of radius 6.34 × 10−15. Each electric charge has a value of 1.60 × 10−19 C. Assuming that the protons create a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, calculate the electric field at the surface of the nucleus.
, has 82 protons within a sphere of radius 6.34 × 10−15. Each electric charge has a value of 1.60 × 10−19 C. Assuming that the protons create a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, calculate the electric field at the surface of the nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charge of uniform density (20 nC/m2) is distributed over a cylindrical surface (radius = 1.0 cm) , and a second coaxial surface (radius = 3.0 cm) carries a uniform charge density of −12 nC/m2. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.0 cm from the symmetry axis of the two surfaces.
A) 0.45 kN/C
B) 1.0 kN/C
C) 0.73 kN/C
D) 0.56 kN/C
E) 2.3 kN/C
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A long cylindrical shell (radius = 2.0 cm) has a charge uniformly distributed on its surface. If the magnitude of the electric field at a point 8.0 cm radially outward from the axis of the shell is 85 N/C, how much charge is distributed on a 2.0-m length of the charged cylindrical surface?
A) 0.38 nC
B) 0.76 nC
C) 0.19 nC
D) 0.57 nC
E) 0.98 nC
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 16-nC charge is distributed uniformly along the x axis from x = 0 to x = 4 m. Which of the following integrals is correct for the magnitude (in N/C) of the electric field at x = +10 m on the x axis?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) none of these
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An uncharged spherical conducting shell surrounds a charge −q at the center of the shell. Then charge +3q is placed on the outside of the shell. When static equilibrium is reached, the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell are respectively
A) +q, −q.
B) −q, +q.
C) +q, +2q.
D) +2q, +q.
E) +3q, 0.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The xy plane is "painted" with a uniform surface charge density which is equal to 40 nC/m2. Consider a spherical surface with a 4.0-cm radius that has a point in the xy plane as its center. What is the electric flux through that part of the spherical surface for which z > 0?
A) 14 N ⋅ m2/C
B) 11 N ⋅ m2/C
C) 17 N ⋅ m2/C
D) 20 N ⋅ m2/C
E) 23 N ⋅ m2/C
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform linear charge density of 4.0 nC/m is distributed along the entire x axis. Consider a spherical (radius = 5.0 cm) surface centered on the origin. Determine the electric flux through this surface.
A) 68 N ⋅ m2/C
B) 62 N ⋅ m2/C
C) 45 N ⋅ m2/C
D) 79 N ⋅ m2/C
E) 23 N ⋅ m2/C
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A charge (uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m) is distributed along the x axis from x = 0 to x = 3.0 m. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point on the x axis with x = 4.0 m.
A) 81 N/C
B) 74 N/C
C) 61 N/C
D) 88 N/C
E) 20 N/C
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each 2.0-m length of a long cylinder (radius = 4.0 mm) has a charge of 4.0 nC distributed uniformly throughout its volume. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 5.0 mm from the axis of the cylinder?
A) 9.9 kN/C
B) 8.1 kN/C
C) 9.0 kN/C
D) 7.2 kN/C
E) 18 kN/C
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electric flux through the two adjacent spherical surfaces shown below is known to be the same.  It is also known that there is no charge inside either spherical surface. We can conclude that
It is also known that there is no charge inside either spherical surface. We can conclude that
A) there is no electric field present in this region of space.
B) there is a constant E field present in this region of space.
C) the electric flux has a constant value of zero.
D) any of the above may be correct.
E) only (a) and (b) above may be correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a cube is inscribed in a sphere of radius r, the length L of a side of the cube is 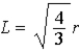 . If a positive point charge Q is placed at the center of the spherical surface, the ratio of the electric flux Φsphere at the spherical surface to the flux Φcube at the surface of the cube is
. If a positive point charge Q is placed at the center of the spherical surface, the ratio of the electric flux Φsphere at the spherical surface to the flux Φcube at the surface of the cube is
A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() .
.
C) 1.
D) ![]() .
.
E) ![]() .
.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A charge of uniform volume density (40 nC/m3) fills a cube with 8.0-cm edges. What is the total electric flux through the surface of this cube?
A) 2.9 N ⋅ m2/C
B) 2.0 N ⋅ m2/C
C) 2.6 N ⋅ m2/C
D) 2.3 N ⋅ m2/C
E) 1.8 N ⋅ m2/C
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 82
Related Exams