A) Electric point
B) Dipolar point
C) Neutral point
D) Isoelectric point
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the separation of a racemic mixture into its component enantiomers called?
A) Diastereomers
B) Meso
C) Resolution
D) Neutralization
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does the formation of salts of a racemic mixture of N-acetyl valine with a single enantiomer of a-methylbenzylamine enable the separation of the two enantiomers of N-acetyl valine?
A) They form amides.
B) They form diastereomers.
C) They form salts.
D) They form meso compounds.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct structure for alanine at pH = 7?
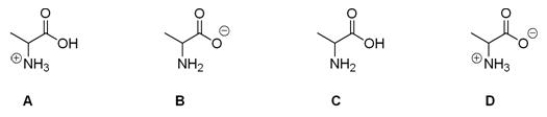
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is formed by the combination of four amino acids?
A) A protein
B) A polypeptide
C) A tripeptide
D) A tetrapeptide
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major organic product for the following reaction?
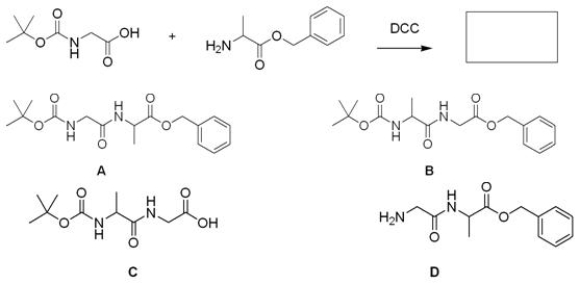
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What reagents would you use to convert acetaldehyde into alanine?
A) NH3
B) HCN
C) NaCN, NH4Cl
D) NaNH2
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following aldehydes would be a good starting material in the Strecker synthesis of phenylalanine?
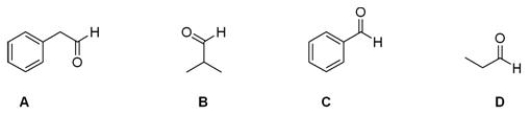
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the correct structure for the amino acid cysteine?
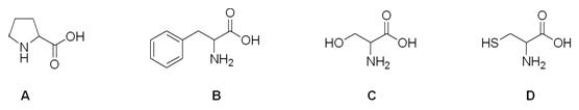
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the configuration of naturally occurring amino acids?
A) D
B) S
C) L
D) R
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly describes the tertiary structure of a peptide?
A) the three-dimensional conformations of localized regions of a protein
B) the particular sequence of amino acids that are joined together by peptide bonds
C) the structure is defined by the b-pleated sheet form
D) the three-dimensional shape adopted by the entire peptide
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do amide bonds exist as reasonably stable s-cis or s-trans isomers at room temperature?
A) These amide bonds are not stable.
B) There is partial double bond character between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen atom.
C) The oxygen atom is hydrogen-bonded with the nitrogen atom.
D) The side-chains can form hydrogen bonds.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds is not an amino acid?
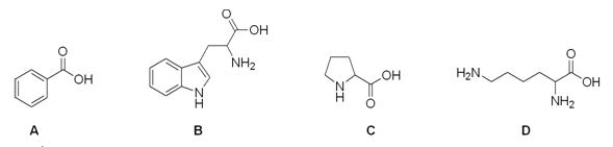
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids does not have an L-isomer?
A) Alanine
B) Valine
C) Glycine
D) Leucine
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amino acid synthesis is possible by all except one of the pathways listed.Which is not a synthetic pathway for amino acids?
A) Amination of malonic ester followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation
B) Nucleophilic addition of NH3 to an aldehyde followed by addition of cyanide to the imine, and, finally, hydrolysis
C) SN2 reaction using an a-halo carboxylic acid with ammonia as the nucleophile
D) Reaction of NH4Cl and NaCN with an aldehyde followed by an acidic work-up
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 35 of 35
Related Exams