A) An economy can produce only on the production possibilities frontier.
B) An economy can produce at any point inside or outside a production possibilities frontier.
C) An economy can produce at any point on or inside the production possibilities frontier, but not outside the frontier.
D) An economy can produce at any point inside the production possibilities frontier, but not on or outside the frontier.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To display information on two variables, an economist must use
A) a bar graph.
B) a pie chart.
C) the coordinate system.
D) a time-series graph.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a variable that is named on an axis of a graph changes, the curve shifts.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Suppose a war in the Middle East interrupts the flow of crude oil and oil prices skyrocket around the world. For economists, this historical episode serves as a
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positive statements are not
A) descriptive.
B) prescriptive.
C) claims about how the world is.
D) made by economists speaking as scientists.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A normative economic statement such as "The minimum wage should be abolished"
A) would likely be made by an economist acting as a scientist.
B) would require values and data to be evaluated.
C) would require data but not values to be evaluated.
D) could not be evaluated by economists acting as policy advisers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2-4
Production Possibilities for Picnicland  -Refer to Table 2-4. What is the opportunity cost to Picnicland of increasing the production of burgers from 450 to 750?
-Refer to Table 2-4. What is the opportunity cost to Picnicland of increasing the production of burgers from 450 to 750?
A) 150 hotdogs
B) 225 hotdogs
C) 300 hotdogs
D) 450 hotdogs
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-15 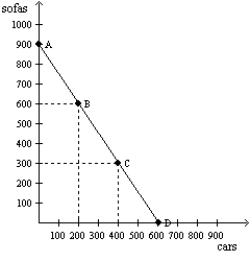 -Refer to Figure 2-15. Consider the production possibilities frontier for an economy that produces only sofas and cars. The opportunity cost of each car is
-Refer to Figure 2-15. Consider the production possibilities frontier for an economy that produces only sofas and cars. The opportunity cost of each car is
A) the slope of the production possibilities frontier.
B) 3/2 sofas.
C) 2/3 of a sofa.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-16 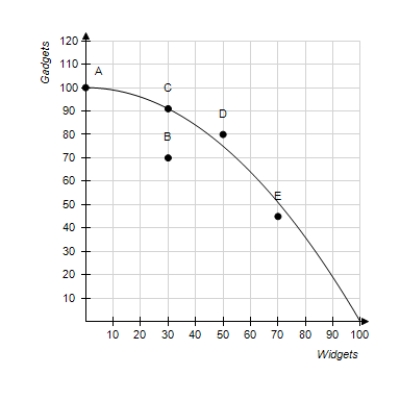 -Refer to Figure 2-16. The opportunity cost of obtaining approximately 20 additional gadgets by moving from point B to point C is
-Refer to Figure 2-16. The opportunity cost of obtaining approximately 20 additional gadgets by moving from point B to point C is
A) 0 widgets.
B) 10 widgets.
C) 20 widgets.
D) none of the above; the economy cannot move from point B to point C.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the circular-flow diagram, one loop represents the flow of goods and services, and the other loop represents the flow of factors of production.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would likely be studied by a macroeconomist rather than a microeconomist?
A) the effect of an increase in the alcohol tax on the market for beer
B) the effect of foreign competition on the domestic auto industry
C) the effect of a price war in the airline industry
D) the effect of an increase in the minimum wage on an economy's overall rate of unemployment
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-7 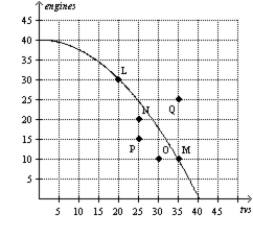 -Refer to Figure 2-7. If this economy moved from point P to point N, then
-Refer to Figure 2-7. If this economy moved from point P to point N, then
A) it still would not be producing efficiently.
B) there would be no gain in either engines or tvs.
C) it would be producing more engines and more tvs than at point P.
D) It is not possible for this economy to move from point P to point N without additional resources.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The language of economics is
A) needlessly arcane.
B) valuable because it provides a new and useful way of learning about the world.
C) easy to learn within a day.
D) unnecessary to learn for a thorough understanding of economics.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If an economy can produce more of one good without giving up any of another good, then the economy's current production point is inefficient.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Figure 2-14 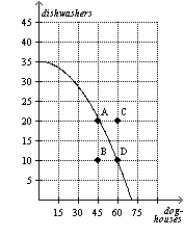 -Refer to Figure 2-14. The opportunity cost of an additional doghouse increases as more doghouses are produced.
-Refer to Figure 2-14. The opportunity cost of an additional doghouse increases as more doghouses are produced.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For economists, substitutes for laboratory experiments often come in the form of
A) natural experiments offered by history.
B) untested theories.
C) "rules of thumb" and other such conveniences.
D) reliance upon the wisdom of elders in the economics profession.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy's production of two goods is efficient if
A) all members of society consume equal portions of the goods.
B) the goods are produced using only some of society's available resources.
C) it is impossible to produce more of one good without producing less of the other.
D) the opportunity cost of producing more of one good is zero.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Figure 2-14  -Refer to Figure 2-14. Given the technology available for manufacturing doghouses and dishwashers, this economy does not have enough of the factors of production to support the level of output represented by point C.
-Refer to Figure 2-14. Given the technology available for manufacturing doghouses and dishwashers, this economy does not have enough of the factors of production to support the level of output represented by point C.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-10
Panel (a)
Panel (b) 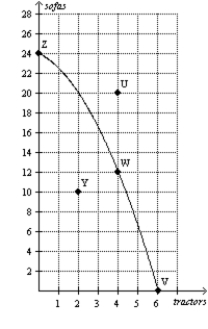
 -Refer to Figure 2-10, Panel (a) . Production is
-Refer to Figure 2-10, Panel (a) . Production is
A) possible at points V, W, Y, and Z, but efficient only at points V, W, and Z.
B) possible at points V, W, Y, and Z, but efficient only at point Y.
C) possible at points U, V, W, and Z, but efficient only at points V, W, and Z.
D) possible at points U, V, W, and Z, but efficient only at point U.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 2-12 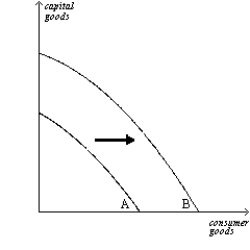 -Refer to Figure 2-12. Which of the following would most likely have caused the production possibilities frontier to shift outward from A to B?
-Refer to Figure 2-12. Which of the following would most likely have caused the production possibilities frontier to shift outward from A to B?
A) a decrease in unemployment
B) a technological advance in the consumer goods industries
C) a general technological advance
D) an increase in the availability of capital-producing resources
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 645
Related Exams